Dec 8, 2025
Smaller Scars, Bigger Impact: The Rise of Minimally Invasive Robotic Heart Surgery
In medical history certain breakthroughs are a complete break with the past. In the field of cardiovascular care this moment is here being celebrated by the advent of minimally invasive robotic heart surgery.
For many years it was the standard procedure for complicated procedures such as valve replacement or bypass surgery requiring the use of a total sternotomy--a massive, painful cut that fractures the breastbone. While it was life-saving, this method was a long, pain-inducing recovery and left a large permanent scar. This method of treatment is constantly being challenged by technological advancement.
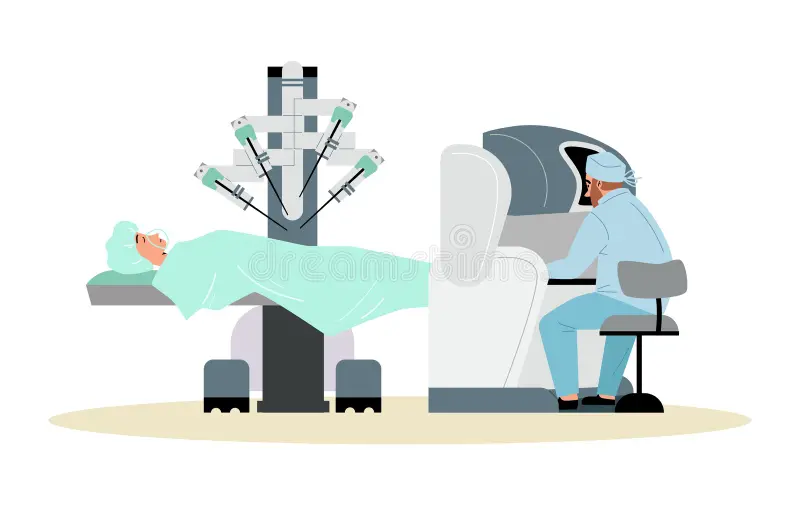
This revolutionary approach leverages technologically advanced robotic surgical equipment to enable the surgeon. Utilizing a specific control panel, a surgeon can control small instruments that are placed through two keyhole-like incisions. This technological leap provides what every patient would like an effective and proven method of open-heart surgery coupled with minimal physical intrusion. This results in a "bigger impact" on the patient's daily life significantly reduced the pain, less blood loss and a lower risk of infections, and a quicker return to normal routine.
This article will examine the way this fusion of robotics and surgical expertise has not only changed the way procedures for the heart are carried out and redefined the overall recovery process and created a brand new, less-traumatic norm for the health of your heart worldwide.
The Surgeon’s Console: Mastering Complexity with 3D Vision and Dexterity
It is the console used by the surgeon. It is the primary operational hub for the robot system. It's typically several feet of the surgical table. The surgeon doesn't stand on top of the patient. Instead, they sit at the console that is ergonomically designed, and put their hands inside specially designed controllers which play the function in the capacity of the guide master. Each move they make is transmitted in real-time, to the robot arms, which are located in an individual's chest. This provides an incredibly comfortable and relaxing environment, which decreases the amount of fatigue suffered by surgeons during long operations.
Immersive 3D High-Definition Vision
The most groundbreaking characteristic is that of the 3D high definition camera that is placed in an incision. The console provides the surgeon with an increased 3-dimensional (3D) view that shows the surgeon's surgical area.
Magnification This view is usually increased by between 10 and 15 times which permits surgeons to see tiny blood vessels and nerves, as well with delicate tissues in a manner that isn't possible with traditional surgery.
Depth Perception In contrast to traditional 2D monitors, 3D displays provide real-time depth perception. This is crucial for jobs such as precise suturing, or delicate tissue dissections, particularly in procedures like valve repair.
Unmatched Dexterity and Precision
Arms of the robot system come equipped with surgical instruments that are specially designed, commonly referred to in the field of EndoWrist instruments. These instruments are akin to and significantly improve the hand's flexibility, with seven degrees of flexibility.
The instruments are equipped with the capability to move and articulate over the limits of the wrist, which allows surgeons to gain access to tight, difficult angles within the chest cavity using small ports.
Tremor Filtration The system eliminates all hand tremors in humans and ensures that only purposeful, pure motions are taken in the center of the person. This degree of accurate, stable accuracy is vital when working with delicate tissues and the structures of the heart.
A surgeon's interface transforms a complex surgical environment into a controlled, improved, completely controlled space that allows surgeons to master complicated cardiac procedures with precision previously unattainable.
Beyond Open-Heart: The Shift from Sternotomy to Keyhole Incisions
In the past, the most sought-after technique for a major operation (like valve repair and bypass) was the sternotomy. It is sometimes called "open-heart" surgery. The surgeon will need to make a 10 to 12 inches diagonal cut through the chest. They then use a specially-designed saw to cut through the chestbone (sternum). Although it is crucial for the heart to fully open, it's a serious injury that has many negatives.
Chronic discomfort, healing and The damaged breastbone requires six to eight weeks to heal completely and may cause extreme post-operative discomfort, and strict restrictions in movements (no pressing, lifting and pulls).
higher chance of developing an the risk of infection An untreated, large wound could increase the chance to develop serious issues, which could include severe wounds to the sternal region.
The scarring is significant. The scar is permanent and noticeable. It could change the appearance of the person who is sporting.
The Robotic Shift: Keyhole Incisions
Robotic surgery doesn't require cutting off a part of the sternum. Instead, surgeons can perform the entire procedure with the aid of three tiny cuts that typically are one or 2 centimeters (less than a quarter of a centimeter) long and are made along the chest's side.
Trauma minimization By avoiding bone splitting or dissection of large muscles bodily injuries are greatly diminished. This is the reason for"Smaller Scars" in your title.
Speedy wound healing The tiny size of wounds mean they heal more quickly, which decreases the risk of infection while also speeding up the speed of healing.
Prioritize recovery In the event that this painful and restrictive portion of open heart procedure (sternum heal) is gone and patients feel less pain and require less opioids. Patients are able to focus on improving the health of the heart, not regaining bone.
The change from a single large sternotomy to a series of keysholes is the most significant advancement that has led to faster recovery times and better outcomes, which make up"the "Bigger Effect" in robotic cardiac surgery.
Precision Bypass: The Revolution of Robotic Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
The development of technological advancements in the field of robotics has revolutionized how surgeons approach Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), the procedure used to alter circulation of blood around coronary arteries that are narrow. While conventional CABG is a full sternotomy and typically using the heart-lung device CABG offers a very effective procedure that is minimally invasive.
The Robotic CABG Procedure
The procedure is usually called "Robotically-Assisted Minimally Invasive Direct Coronary Artery Bypass (RA-MIDCAB). It's typically performed in two key phases:
Achieving Graft Harvesting with Precision: The enhanced visualization of the robot is essential to ensure safe and complete removal from the Left Mammary Artery (LIMA) out of the chest. This is because the LIMA is the most popular site for grafting the right Anterior Descending (LAD) coronary artery because of its durability as well as its stabilities. Robotic arms gently cut the artery through tiny ports, minimizing the damage to the tissue surrounding it. This is not feasible or even feasible by making tiny cuts without the aid of robotics.
Beat-Heart Anastomosis: Often the robotic CABG is performed in the running heart (off-pump) which removes the requirement for a heart-lung machine, as in addition to its potential dangers. The surgeon uses exact-controlled tools to stitch the LIMA graft onto the coronary artery which is blocked by the blockage below. This procedure, which is called anastomosis, demands the most precise level of accuracy and ease of use due to the robot's steady movements that are free of tremors, and upgraded 3D-image.
Key Advantages Over Traditional CABG
The shift to robotic assistance provides significant advantages in terms of clinical outcomes, but without compromising the durability of procedures themselves.
Minimized Trauma The procedure is carried out through the application of three to four small cut (keyholes) inside an artery in the chest that is in between the ribs without Sternotomy and the long, painful recovery time.
Reduces complications The low-risk of being surgically invasive implies reduced blood loss as well as a less chance of developing infections and a lesser need for the need for blood transfusions.
Rapider recuperation: Patients generally experience less discomfort and may experience a less lengthy hospital stay (often three to four days) and a quicker return to routines and activities when compared with the amount of time required for the recovery process following a surgery-related sternotomy.
Robotic CABG is generally the best choice for patients that require one or two-vessel bypass, particularly those that require an LAD-related artery. It has been proven to be the most suitable procedure for those who meet the criteria and are have been selected.
Healing the Valves: Minimal Access for Mitral and Tricuspid Valve Repair
It is the Mitral valve, which is located between the left chambers of the heart as well as the Tricuspid valve, located between the right chambers, that play crucial for controlling blood flow. When these valves begin to leak (regurgitation) or narrowed (stenosis) they need to be repaired or replaced.
Traditional valve surgery requires the making of a huge cutting and opening of the ribcage for access and see-through. The robotic surgery removes this crucial step.
Robotics: Precision in the Tightest Spaces
Instead of a large lung opening in the chest, the surgeon makes use of the robot by making tiny cut-outs (keyholes) located on either chest's left side. This allows for a clear view and direct access to the valves without damaging the ribs or sternum.
Superior Visualization The magnified HD 3-D camera is essential for this. The tissue of the valve is intricate and delicate The magnified view enables surgeons to see delicate structures of the chords and leaflets with incredible clarity, allowing them to pinpoint the precise site of the problem.
Maximum Dexterity The articulating, fine EndoWrist instruments enable surgeons to execute the precise maneuvers needed to repair the damage:
Redesigning leaflets.
Reconnecting broken chords.
Inserting An annuloplasty band to strengthen the valve.
The actions required are exact suturing and knot-tying within an area that is cramped, and are made possible thanks to the extremely flexible and tremor-free robotic arms.
The Patient Advantage
The use of robotic method offers significant benefits for patients who are undergoing valve repairs:
There is no sternotomy pain. Reducing the risk of splitting the breastbone, patients can avoid the most painful part of recovery, which allows them to heal from the valve repair much more quickly.
Reduced Blood Loss A minimal tissue dissection leads to significantly less loss of blood and less requirement to receive blood transfusions.
Rapider mobilization: Patients are usually capable of leaving the hospital earlier (often 3 to 5 days) and resume normal, non-strenuous activities faster than after open heart surgery.
The Swift Recovery Promise: Shorter Hospital Stays and Faster Return to Life
The most obvious benefit to patients who undergo robotic heart surgery is the rapid acceleration of their recovery time. The absence of a complete surgical sternotomy (splitting your breastbone) the most significant source of pain and limitation is eliminated completely, transforming the post-operative patient's experience.
Reducing the Hospital Stay
The traditional open heart surgery patients typically require 7 to 10 days in the hospital and the first few days are being devoted to managing the severe discomfort and monitoring the healing process of the incision on their sternum.
Robotic Surgery Advantages: Patients undergoing robotic procedures, like repairs to the valve or CABG typically experience a considerably smaller hospitalization that can range between 3 to five days. This can be achieved due to less trauma inside, less blood loss, and significantly lower risk of serious wound complications.
Accelerated Mobilization: With no possibility of a non-union or an infection due to a cracked sternum the patient can be moved earlier. Patients are generally advised to walk, and start cardiac rehabilitation exercises almost immediately following surgery.
Accelerating the Return to Daily Life
The difference in the home-based recovery is also significant which defines"the "Bigger Impact" on the patient's health and quality of life.
Recovery Milestone | Traditional Open-Heart Surgery (Sternotomy) | Robotic Cardiac Surgery (Keyhole Incision) |
Pain Management | It requires strong narcotics over several weeks. | It is easily treated with over-the-counter medications or mild painkillers shortly after the discharge. |
Lifting Restriction | Strenuous 6-to-8-week restriction on lifting any weight greater than 5-10 pounds (to let the sternum join). | Restrictions are typically less severe and last a shorter time (often 1-2 weeks) which allows for earlier participation in the daily activities. |
Return to Work | Most often, it takes typically 8 to twelve days off, based on the demands of the job. | Many patients go back to work or sedentary within two to four weeks. |
Driving | Typically, the prohibition is typically for between 6 and 8 days (due to the possibility of airbag injury and sternum healing). | Most often, it is resumed within two to three weeks. |
Clinical Wins: Minimizing Blood Loss, Pain, and the Risk of Infection
In addition to the speedy recovery and less scars, the main benefit of robotic surgery for cardiac conditions is in the quantifiable clinical successes which improve the safety of patients and improve outcomes. These advantages are directly related to the low-invasive nature of the procedure that minimizes the injury for the human body.
Minimizing Blood Loss
One of the primary measures in determining the safety of surgery is volume of blood loss during the procedure.
precision dissection Robotic arms that are guided through the enhanced 3-D vision allows for highly precise dissection and handling of tissue. This precise control aids the surgeon maneuver around important blood vessels.
reduced vessel trauma Through tiny ports rather than creating large incisions or retracting the ribs, there is substantially lower injury to the muscles around and the small blood vessels.
End-Result: Patients typically experience less blood loss during the procedure and, as a result suffer a less requirement to receive blood transfusions in comparison to open-heart surgery. This decreases the risks of transfusions and helps the patient's speedy recovery.
Drastic Reduction in Pain
The most common reason for prolonged, severe post-operative discomfort in conventional heart surgery is the sternotomy (splitting in the breastbone).
Preventing Bone Trauma: Robotic surgery completely does not involve cutting or breaking the sternum. This will eliminate the cause of the most severe, ongoing discomfort and the limiting recovery time that is associated with bone fusion.
Targeted Incisions Because the incisions are tiny (keyhole dimensions) and are placed between the ribs, the muscle damage is not significant.
End-of-life: Patients report significantly less pain post-operatively and are required to take less or less narcotic painkillers following the discharge. This enables them to participate with rehabilitation, and to return to active life sooner.
Lowering the Risk of Infection
The risk of infection at the surgical site is an extremely serious problem in any procedure, however the risk is significantly decreased with the use of robotics.
Reduced exposure: The surgical field is exposed to the outside surroundings for a significantly shorter amount of time. The surgical incisions are quickly sealed.
The Small Wound Area The main risk with conventional surgery is a deep sternal injury which could be life-threatening. Utilizing a series of tiny incisions instead of a larger deep sternotomy, the area of the wound that is susceptible to infection is greatly diminished.
Results: The decreased trauma and less wounds lead to a lower risk of deep as well as superficial infections which ensures a more secure healing process.
The clinical benefits that these fundamental advantages offer -- less bleeding, more painless, less risk of infection -- are the reason why robotic cardiac surgery is advancing towards being an accepted standard of medical treatment for patients who are eligible.
The Candidate Criteria: Who is Best Suited for Robotic Heart Surgery?
Although robotic heart surgery has many advantages, it's not a common procedure. Selection of the patient is a crucial stage that requires careful analysis and imaging in order to ensure that the procedure is compatible with your anatomy and extent of their medical condition.
Eligibility for Robotic Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
A robot CABG is a highly efficient method, however, the way it is used is generally targeted and precise.
conditions for vessels: It's ideal for patients who require a double or single vessel bypass especially when it is related to the crucial Left anterior descending (LAD) heart.
Heart Function People who are eligible typically are those with good cardiac function (ejection fraction).
condition of Calcification Patients should not be suffering from significant calcifications of veins that supply blood to the coronary artery. A calcification may make the delicate operation of robots more difficult and, in some instances, may require a different approach.
Eligibility for Robotic Mitral and Tricuspid Valve Surgery
Valve procedures comprise among the widely utilized and successful surgical methods. The majority of patients suffering from these issues can benefit from these procedures:
Mitral Valve Prolapse A condition that occurs frequently where valve leaflets expand prior to retracting back into the chamber of the heart.
Severe Mitral Resurgitation A condition in which the valve is leaky.
Mitral Stenosis A condition in which the valve narrows.
Tricuspid Valve Disease: Similar problems (regurgitation or stenosis) because of the valve on its right side.
Limitations on Exclusion Similar to those for CABG Patients shouldn't be suffering from huge calcium calcification and/or any structural or anatomical problems that might hinder the robot's mobility and accessibility.
General Considerations
The final decision is made after a thorough review of the medical staff that performs the cardiac surgery, using certain photographs (like CT scans and echocardiograms). Some items that can aid a patient to be appropriate for open heart surgery include:
The requirement for a multiple-vessel Bypass Patients who have blockages that are difficult to treat and require at least three transplants, are usually treated with a standard approach.
A large previous surgery A chest surgery you've had prior to the big one can create adhesions that could hinder your ability to undergo surgery robotics.
serious Aortic disease: Extensive disease or calcification of Aorta may make it difficult to obtain a minimally surgical procedure.
Unseen Advantages: Enhanced Ergonomics and Tremor-Free Surgical Control
The shift to robotic assisted surgery has significant advantages, but it also offers some obscurities which are linked to the surgeon's physical flexibility and accuracy. As previously stated, the "unseen advantages" are critical in the case of long, high-risk procedures.
Enhanced Ergonomics for the Surgeon
Standard and traditional laparoscopic surgery generally requires surgeons to be in uncomfortable stiff and difficult positions over an extended period of. This can cause constant pain, fatigue and musculoskeletal problems that can hinder your work.
The postures of robots, which are natural like the da Vinci system, allows surgeons to operate from a seated position on operating consoles. The arms and hands of the surgeon are supported by support mechanisms and wrist controls that mimic an ergonomic and natural position .
Lowering physical strain robots are capable of handling the high lifting as well as manipulation and the countertraction. This reduces the physical strain associated with keeping instruments in place and retracting tissue for long durations in time.
Enhances capacity and focus Through the elimination of body-related discomforts surgeons are capable of keeping greater levels of focus and endurance during long or complicated cases, which enhances how decisions are taken and the outcomes for patients.
Tremor-Free Surgical Control
One of the biggest benefits of robots is their complete elimination from hand shaking and the ability to control the motion of a way which is not possible using a hand unsupported.
Tremor Filtration Software of the robotic system removes all subtle and natural movement ( five to 10 Hz in Hz dollars) that we humans suffer from. The surgeon is provided with the ideal instruments that have constant tips that are essential when working with delicate and small structures such as blood vessels, nerves, and even blood vessels that are tiny.
Motion Scaling Hand movements from the surgical surgeon can be reduced by a factor of the machine (e.g. the 4mm motion on the console could be transformed into a millimeter in the body of a patient's ).> This allows precise and precise manipulation which is way beyond human capabilities, particularly for working within tight areas.
Stability when fatigued Although the hands of surgeons might be tired during an extended procedure The robotic arms maintain their preset stability and accuracy and ensure constant motions from start to end.
These two factors--improved physical well-being for the surgeon and superior motion control--collectively contribute to safer, more consistent, and ultimately more effective surgical care.
The Evolution is Now: Why Robotic Surgery is the Standard for Selected Patients
Robotics integration into surgery is not merely a flimsy trend that is a sign of the future major development for minimally invasive surgeries (MIS). 1 In an ever-growing number of complicated procedures, robotic-assisted surgery is now the preferred method of treatment for certain patients because of its capability to deliver superior results in areas when human dexterity, vision and strength are the most difficult.
Bridging the Gap: Complex Procedures Become Minimally Invasive
The main reason that makes robotic surgery the current standard is its ability to perform traditional challenging and impossible minimally invasive procedures with increased accuracy. 2
Overcoming Laparoscopic Limitations: Traditional laparoscopy utilizes rigid instruments that have a restricted movement range (four degree of freedom).3 Robotic systems, including the EndoWrist instruments, have seven degree of freedom that mimic the sensitivity of a human wrist but on a miniature scale.4 This allows for more complex maneuvers such as fine dissection and deep suturing within restricted anatomical spaces.5
The power of 3D Vision: The system supplies the surgeon with a magnified, high-definition, 3D perspective of their operating area. 6 This sharpness and depth perception is essential for the identification and preservation of delicate structures such as blood vessels and nerves, which are difficult to see using the two-dimensional view of laparoscopy. 7
Key Areas Where Robotics is the Standard
For procedures that require extreme accuracy in delicate or small areas, robotics has replaced conventional open or standard laparoscopic methods due to the demonstrable advantages in the patient's outcomes.
Surgical Specialty | Standard-Setting Procedures | Key Outcome Advantage |
Urology | Radial Prostatectomy (prostate removal of cancer) | Neuron Preservation which allows for a faster return of Erectile function and urinary continence. |
Gynecology | Hysterectomy, Myomectomy (fibroid removal) | Reduction in loss of blood and the capability to perform complicated procedures using smaller incisions. |
Colorectal | Colectomy (colon resection) | Fine suturing and superior access within the tiniest bladder which reduces the need for open surgery. |
Cardiothoracic | Lobectomy (lung cancer), Mitral Valve Repair | It allows for the least invasive access to the chest cavity which reduces the risk of injury to ribs and the sternum. |
Benefits Translating to the New Patient Expectation
For patients who are patients, their "standard of care" is today heavily influenced by minimally invasive benefits that the robotic platform offers:
Quicker Recovery and Shorter stays: Due to smaller and more precise incisions there is lower trauma to the surrounding tissue. 8 This usually results in:
Lower Post-Op Pain: Requiring fewer narcotic pain medication. 9
Shorter Hospital Stays: Often allowing same-day or next-day discharge.10
Faster return to normal activity: Enabling a faster resume of everyday work and daily life. 11
Lower Complication Rates Improved visualization and precision reduces the chance of damage to vital structures, resulting in lesser rates of complications like bleeding and infection when compared to traditional open surgery. 12
The synergy of surgical ability (dexterity as well as vision) and the outcome for patients (faster recovery, less complications) is what makes robot surgery the most preferred option for a growing number of intricate procedures, which has solidified its status as a modern standard for surgical patients.
This is done through not having a complete surgery called sternotomy (splitting the bone) that can be the most uncomfortable and restricting part of open-heart surgery. Instead, the surgeon will perform the procedure by making tiny "keyhole" incisions.
Key Advantages of the Robotic Approach:
Feature | Description | Patient Impact |
Precision & Visualization | The instruments controlled by a surgeon operate with the use of a 3-D high definition camera along with the magnified view of the heart. | Allows for astonishing precision for delicate tasks such as fine suturing as well as tissue repair vital for valve surgery. |
Minimal Invasiveness | Procedures are carried out using tiny keyhole cuts, eliminating any need to cut the breastbone. | It results in less suffering, minimal blood loss which means reduces the risk of bleeding, and less chance of infections and wound-related complications. |
Accelerated Recovery | The mammary artery in the internal (IMA) is extracted using precision and minimal trauma is sustained during the robotic CABG. | This results in lower hospitalization (often 3 to 5 days) and a considerably quicker return to normal activities or work. |
Procedures and Candidate Selection:
The site states that robotic surgery has been proven to be a successful method for:
ROBOTIC CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting): Best suited for patients who require either a single or double vessel bypass, specifically ones that affect the anterior descender of the left arterial.
The Robotic Mitral Valve Surgery: Perfect for conditions such as regurgitation that is severe, prolapse or stenosis as long as there isn't a lot of calcification.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is robotic cardiac surgery?
Robotic cardiac surgery is a minimally invasive procedure where the surgeon controls robotic instruments through a console to perform precise heart operations. It uses tiny incisions instead of a large chest opening, allowing for faster recovery and minimal scarring.
2. How is robotic heart surgery different from traditional open-heart surgery?
Traditional surgery requires a sternotomy (cutting through the breastbone), while robotic surgery uses keyhole-sized incisions between the ribs. This means less trauma, reduced blood loss, fewer complications, and quicker healing compared to conventional methods.
3. Who is an ideal candidate for robotic cardiac surgery?
Ideal candidates typically include patients needing mitral or tricuspid valve repair, atrial septal defect (ASD) closure, or coronary artery bypass (CABG) — especially those without extensive calcification or severe chest deformities. A detailed evaluation by a cardiac surgeon like Dr. Rehan Sayeed helps determine suitability.
4. Is robotic cardiac surgery safe?
Yes. Robotic cardiac surgery is highly safe and effective when performed by experienced surgeons. The robot doesn’t operate autonomously — every movement is precisely controlled by the surgeon, ensuring complete human oversight throughout the procedure.
5. What are the main benefits for patients?
Minimal scarring and better cosmetic results
Reduced pain and discomfort
Shorter hospital stay (often 3–5 days)
Faster recovery and return to normal activities
Lower risk of infection and complications
6. How long does the surgery take?
The duration may vary depending on the complexity of the case, but most robotic cardiac surgeries last between 3 to 5 hours. While setup time can be longer initially, overall recovery time is significantly shorter.
7. How long is the recovery period?
Patients usually recover within 2–3 weeks, compared to 6–8 weeks for traditional open-heart surgery. Most return to daily routines and light work much sooner.
8. Are the results as good as traditional surgery?
Yes, studies show that outcomes are equal or superior to traditional surgery in many cases, especially in valve repairs. The precision, stability, and visibility offered by the robotic system often lead to better surgical accuracy.
9. What kind of robot is used for heart surgery?
The da Vinci Surgical System is the most widely used robotic platform. It provides 3D high-definition visualization, enhanced dexterity, and tremor-free instrument movement, allowing surgeons to perform delicate cardiac repairs with remarkable accuracy.
10. Are there any limitations or risks?
As with any surgery, risks like bleeding, infection, or reaction to anesthesia exist, though they are significantly lower with robotic methods. Certain patients (e.g., those with extensive previous chest surgeries or complex anatomy) may not be suitable candidates.
11. How do I know if robotic cardiac surgery is right for me?
A consultation with a specialized robotic cardiac surgeon — such as Dr. Rehan Sayeed — is essential. He will perform a thorough clinical and imaging assessment to determine if the minimally invasive robotic approach is the best option for your specific heart condition.