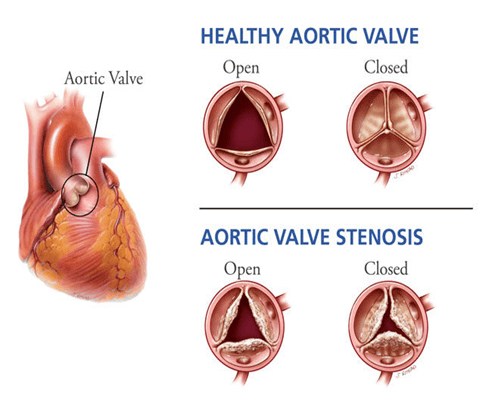
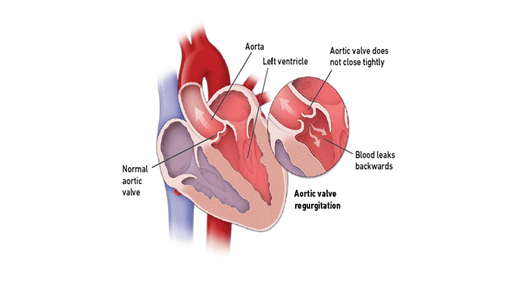
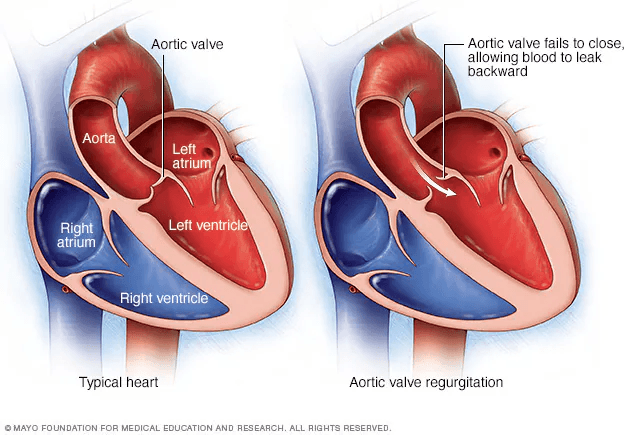
Aortic Valve disease refers to any condition that affects the function of the aortic valve,which controls blood flow from the left ventricle of the heart into the aorta and onward to the rest of the body
Leakage of the valve of the valve leading to backflow of blood from aorta to ventricle (backward to the heart)
CAUSES
Valve degenration
Infection (endocarditis)
trauma
SYMPTOMS:
Dyspnea( shortness of breath)
Fatigue ( tiredness)
Palpitations
Heart failure symptoms ( odema – swollen ankles in later stages)
DIAGNOSIS
NOW
• ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY : to asses valve anatomy and function and ventricle function
• ECG
• CHEST XRAY
• Cardiac CT :structural details and planning for surgery
• Cardiac CT :structural details and planning for surgery
Treatment strategies depend on the severity of the condition, presence of symptoms, the specific type of aortic valve disease, and the patient's overall health
MANAGEMENT
Early stages:
Mild or moderate cases, or asymptomatic patients, may only require regular monitoring and lifestyle modifications.h
Medications:
Can help manage symptoms, but don't cure the disease or reverse valve damage
Lifestyle adjustments:
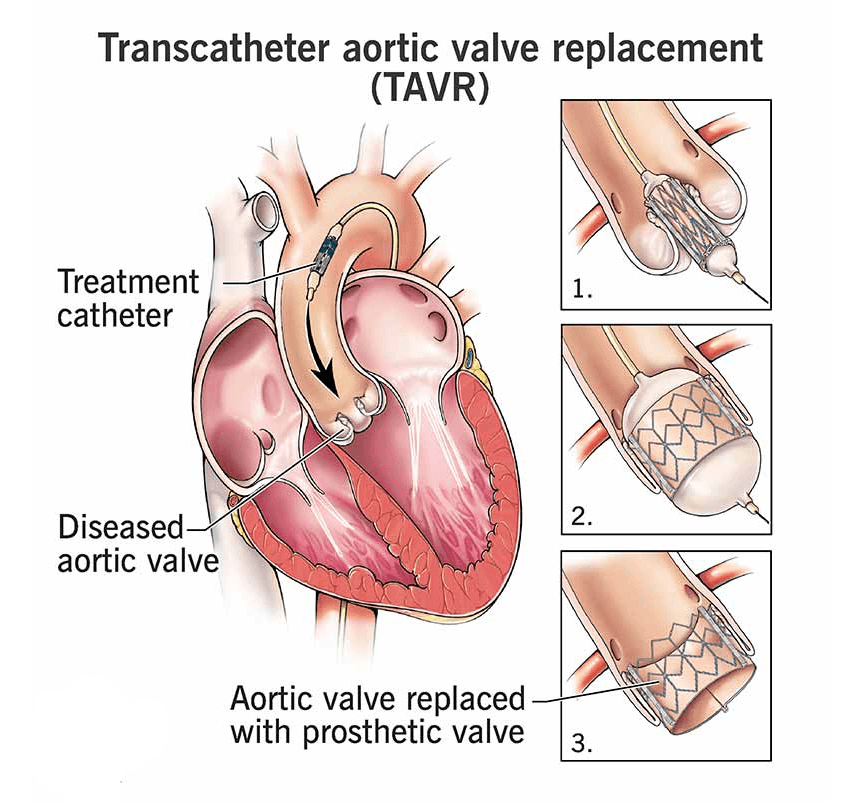
A minimally invasive procedure where a new valve is implanted using a catheter, typically inserted via a blood vessel in the leg or groin. TAVR is often an option for patients considered ata very high risk for traditional open-heart surgery.
POST OPERATIVE MANAGEMNT
NOW
• Rehabilitation – walking , stair climbing, chest physiotherapy, spirometry wound care
• Dietary restrictions for patients on acitrom
• Mechanical valve – regular INR monitoring
Prognosis
NOW
The prognosis for aortic valve disease depends heavily on the severity of the condition and the timing of intervention. Untreated, severe aortic stenosis can lead to a significantly reduced life expectancy. However, with appropriate medical management and timely surgical or interventional procedures, many individuals can lead active and fulfilling lives.
Aortic Stenosis (AS)
For severe cases, particularly if symptoms are present or the heart function is impacted, surgical procedures may be necessary
Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (AVR):
Replaces the damaged valve with a prosthetic valve.
Approaches to surgery
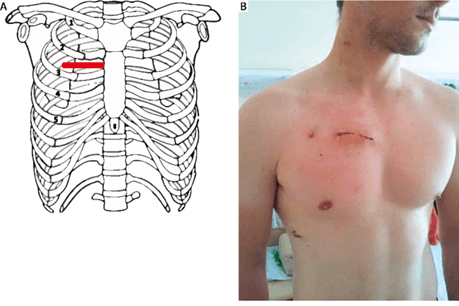
RAT (right anterior thoracotomy)
5-7 cm incision in the 2nd or 3 rd ICS on right side of chest disease
Advantages:
Minimally invasive : preserves sternum
less pain
faster recovery
shorter hospital stay
cosmesis
Heart failure symptoms ( odema – swelling , orthopnea
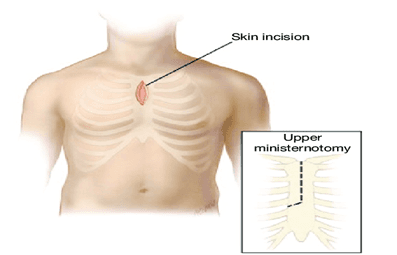
5 cm incision in the upper 1/3 rd of sternum J shaped
Advantages
Less invasive than full steromy in terms of recovery and cosmesis
Shorter operative time
CONVENTIONAL OPEN SURGERY
15 cm incision dividing the sterum in the midline
Advantages
More invasive
Long recovery
More pain
Large scar

Virtual Care
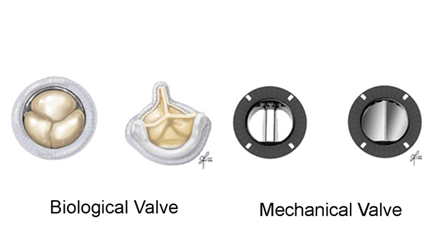
Mechanical valves
Durable but require lifelong blood thinners and monitoring